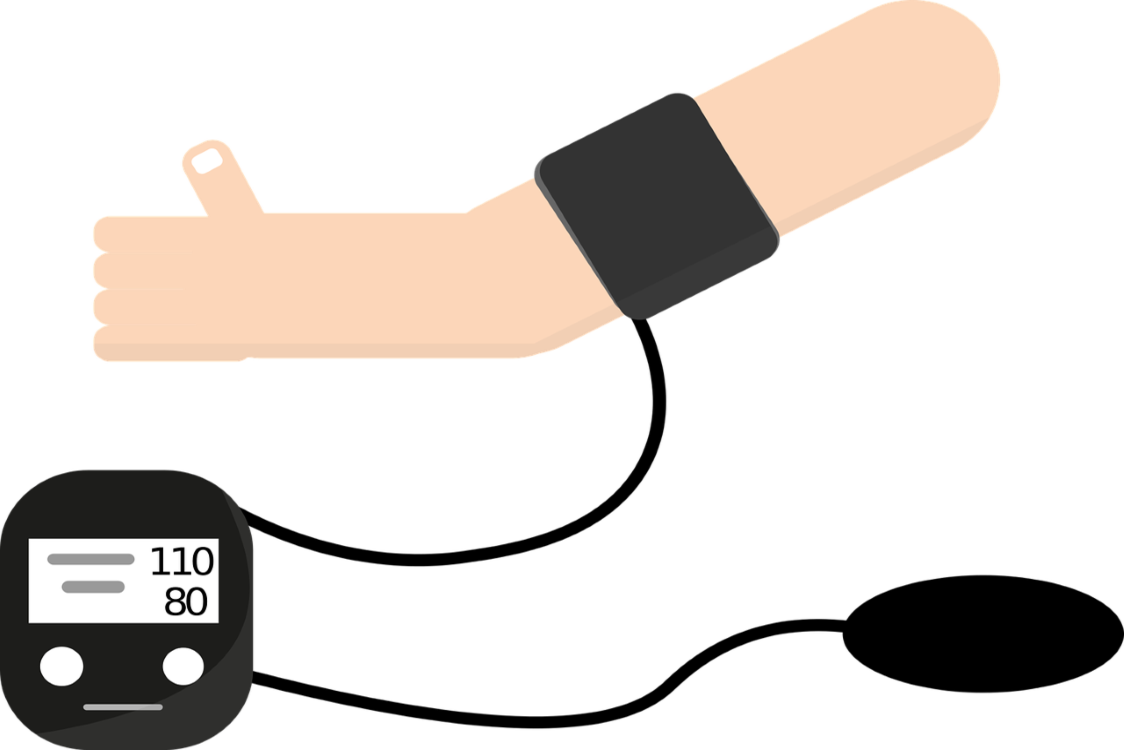
It is very important to know how to measure blood pressure. Various studies have shown that the higher the blood pressure, the greater the cardiovascular risk. As blood pressure increases, the risk of stroke, heart disease and peripheral artery disease, as well as the incidence of death from cardiovascular causes, progressively increases. Therefore, it is essential to normalize blood pressure.
In order to control high blood pressure, you need to know how to measure blood pressure correctly and reliably:
1. The patient should be relaxed, sitting in a chair with feet on the floor and back supported for more than 5 minutes.
2. The patient should not consume caffeine, exercise, or smoke for at least 30 minutes before the measurement.
3. The patient must have previously emptied his bladder.
4. Neither the patient nor the observer should talk during the rest period or during the measurement.
5. Remove all clothing covering the area of the arm where the cuff will be placed.
6. Measurements made while the patient is sitting or lying on a table or bed where the physical examination is being performed do not meet these criteria.
7. A blood pressure measuring device that has been validated and periodically calibrated should be used.
8. The patient’s arm should be supported on a table.
9. The middle part of the cuff should be placed on the patient’s upper arm at the level of the right atrium (the midpoint of the sternum).
10. The correct size of cuff must be used, so that it surrounds 80% of the arm.
11. Initially, blood pressure should be measured in both arms and in future follow-up measurements will be taken in the arm that shows higher blood pressure.
12. The cuff should be deflated at a rate of 2 mm Hg per second.
13. An average of 2 or more readings taken on 2 or more occasions should be used to estimate an individual’s blood pressure level.
Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension